Simple:4w83q2xii9q= Prokaryotic Cell represent a fascinating area of study within microbiology, distinguished by their lack of membrane-bound organelles and unique genetic structures. These organisms, often perceived as simplistic, actually exhibit a remarkable range of metabolic functions and adaptability, enabling them to occupy diverse ecological niches. Their roles extend beyond mere survival; prokaryotes are integral to nutrient cycling and maintain ecosystem balance. Additionally, their presence in the human microbiome raises intriguing questions about their influence on health and disease. What further complexities might emerge when examining their interactions within various environments?
Characteristics of Prokaryotic Cells
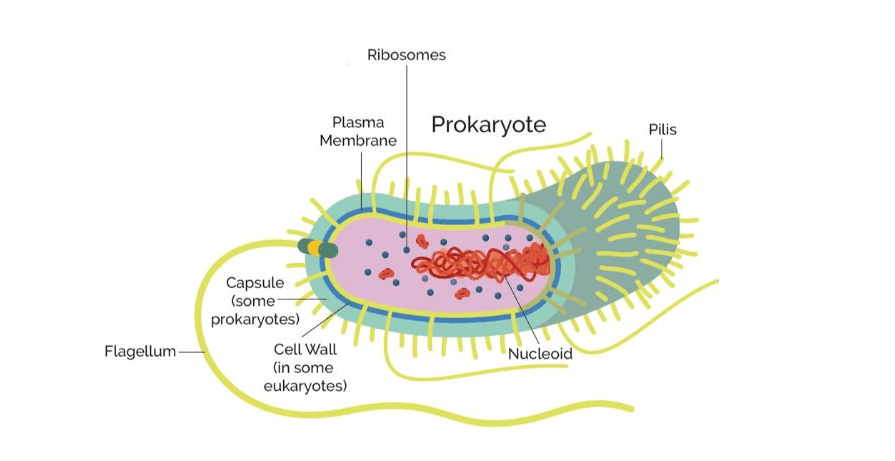
Prokaryotic cells, characterized by their lack of a membrane-bound nucleus, exhibit fundamental differences from eukaryotic cells that have significant implications for their biology and ecology.
Their cell structure is simpler, typically comprising a single circular chromosome that contains their genetic material, located in the nucleoid region.
Additionally, prokaryotes often possess plasmids, which further diversify their genetic capabilities and functional adaptability.
Functions and Processes
In the realm of cellular biology, the functions and processes of prokaryotic cells are essential to understanding their role in various ecosystems and their adaptability to diverse environments.
Prokaryotic cells utilize their genetic material, typically organized in a single circular chromosome, to regulate cellular respiration and metabolic pathways, enabling them to efficiently convert nutrients into energy and respond dynamically to environmental changes.
Diversity in Prokaryotic Life
The remarkable adaptability of prokaryotic cells is reflected in their extensive diversity, which encompasses a wide range of shapes, sizes, and metabolic capabilities.
This diversity is a product of prokaryotic evolution, allowing organisms to thrive in various environments.
Metabolic diversity enables prokaryotes to utilize different substrates for energy, contributing to their ecological versatility and evolutionary success across diverse habitats.
Read Also Simple:4qrrzquz2uy= Resignation Letter Template
Role in Ecosystems and Health
Numerous prokaryotic organisms play crucial roles in both ecosystems and human health, acting as fundamental components of biogeochemical cycles and influencing the dynamics of various habitats.
Prokaryotic symbiosis enhances nutrient availability and promotes microbial metabolism, essential for organic matter decomposition and nutrient recycling. Their interactions underpin ecosystem stability, while also supporting human health through gut microbiota, which influences digestion and immune responses.
Conclusion
In summary, Simple:4w83q2xii9q= Prokaryotic Cell serve as the foundational building blocks of life, exhibiting remarkable simplicity yet profound complexity in their functions. These microscopic entities, like unseen architects, orchestrate intricate processes within ecosystems and contribute significantly to human health. Their diverse forms and metabolic capabilities enable them to adapt to various environments, ensuring their survival and pivotal roles in nutrient cycling. Ultimately, prokaryotes underscore the interconnectedness of life, highlighting their indispensable contributions to both ecological stability and human well-being.
